Icy fingers and toes: Poor circulation or Raynaud’s phenomenon?
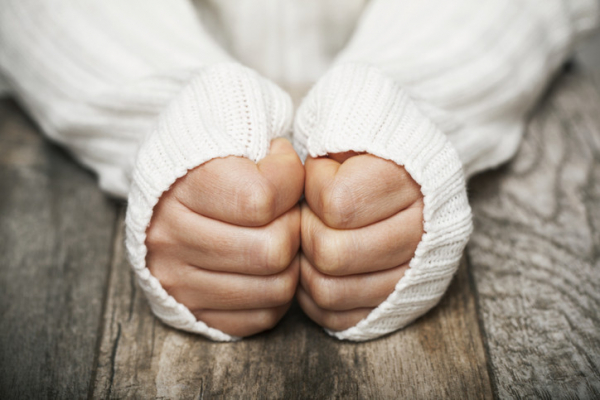

If your fingers or toes ever turn pale (or even ghostly white) and go numb when exposed to cold, you might assume you just have poor circulation. That’s what I used to think when I first started noticing this problem with my own hands many years ago.
It usually happened near the end of a long hike on a spring or fall afternoon, when the temperature dropped and I didn’t have any gloves handy. My pinkie, third, and middle fingers would turn white, and the fingernails took on a bluish tinge. As I soon discovered, I have Raynaud’s phenomenon, an exaggeration of normal blood vessel constriction.
Raynaud’s phenomenon: Beyond poor circulation
When you’re exposed to a cold environment, your body reacts by trying to preserve your core temperature. Blood vessels near the surface of your skin constrict, redirecting blood flow deeper into the body. If you have Raynaud’s phenomenon, this process is more extreme.
Is wintry weather the only trigger for Raynaud’s phenomenon?
“Cold weather is the classic trigger for Raynaud’s phenomenon," says rheumatologist Dr. Robert H. Shmerling, senior faculty editor at Harvard Medical School's Harvard Health Publishing.
"But it can occur any time of year — for example, when you come out of a heated pool, walk into an air-conditioned building, or reach into the freezer section at the supermarket. Even slight changes in air temperature can trigger an episode.”
What happens when an episode occurs?
During an episode, the small arteries supplying the fingers and toes contract spasmodically, hampering the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the skin. Some of these vessels even temporarily collapse, and the skin becomes pale and cool, sometimes blanching to a stark white color.
In addition to the hands, Raynaud’s can also affect the feet. Less often, the nose, lips, and ears.
Is Raynaud’s phenomenon a circulation problem?
Technically, Raynaud’s phenomenon is a circulation problem, but it’s very different than what doctors typically mean by poor circulation, says Dr. Shmerling. Limited or poor circulation usually affects older people whose arteries are narrowed with fatty plaque (known as atherosclerosis). This condition is often caused by high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and smoking.
In contrast, Raynaud’s usually affects younger people (mostly women) without those issues. And the circulation glitch is generally temporary and completely reversible, he adds.
How can you prevent episodes?
As I can attest, the best treatment for this condition is to prevent episodes in the first place, mainly by avoiding sudden or unprotected exposure to cold temperatures. I’ve always bundled up in the winter before heading outside, but now I bring extra layers and gloves even when the temperature might dip even slightly, or the weather may turn rainy or windy. Preheating the car in winter before getting in, and wearing gloves in chilly grocery store aisles, can also help.
Generally, it’s best to avoid behavior and medicines that cause blood vessels to constrict. This includes not smoking and not taking certain medications, such as cold and allergy formulas that contain pseudoephedrine and migraine drugs that contain ergotamine. Emotional stress may also provoke an episode of Raynaud’s, so consider tools and techniques that can help you ease stress, such as mindfulness techniques.
If necessary, your doctor may prescribe a medication that relaxes the blood vessels, usually a calcium-channel blocker such as nifedipine (Adalat, Procardia). If that’s not effective, drugs to treat erectile dysfunction such as sildenafil (Viagra) may help somewhat. Other treatment options include losartan (Cozaar), fluoxetine (Prozac), and topical nitroglycerin. You may only need to use these medications during the cold season, when Raynaud’s tends to be worse.
What steps may help during an episode?
Once an episode starts, it’s important to warm up the affected extremities as quickly as possible. For me, placing my hands under warm running water does the trick.
When that’s not possible, you can put them under your armpits or next to another warm part of your body. When the blood vessels finally relax and blood flow resumes, the skin becomes warm and flushed — and very red. The fingers or toes may throb or tingle.
Is Raynaud’s phenomenon linked to other health problems?
Some people with Raynaud’s phenomenon have other health problems, usually connective tissue disorders such as lupus or scleroderma. Your doctor can determine this by reviewing your symptoms, performing a physical exam, and taking a few blood tests. But most of the time, there is no underlying medical problem.
About the Author

Julie Corliss, Executive Editor, Harvard Heart Letter
Julie Corliss is the executive editor of the Harvard Heart Letter. Before working at Harvard, she was a medical writer and editor at HealthNews, a consumer newsletter affiliated with The New England Journal of Medicine. She … See Full Bio View all posts by Julie Corliss
About the Reviewer

Howard E. LeWine, MD, Chief Medical Editor, Harvard Health Publishing
Dr. Howard LeWine is a practicing internist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Chief Medical Editor at Harvard Health Publishing, and editor in chief of Harvard Men’s Health Watch. See Full Bio View all posts by Howard E. LeWine, MD